Thigh Muscles: The thigh is the area between the hip and the knee joint. It is part of the lower limb. The single bone in the thigh region is called the femur. This bone is very thick and strong and makes a ball and socket joint at the hip, and a hinge joint at the knee. Muscles of the thigh divided into three compartment-
- Anterior Compartment
- Posterior Compartment
- Medial Compartment
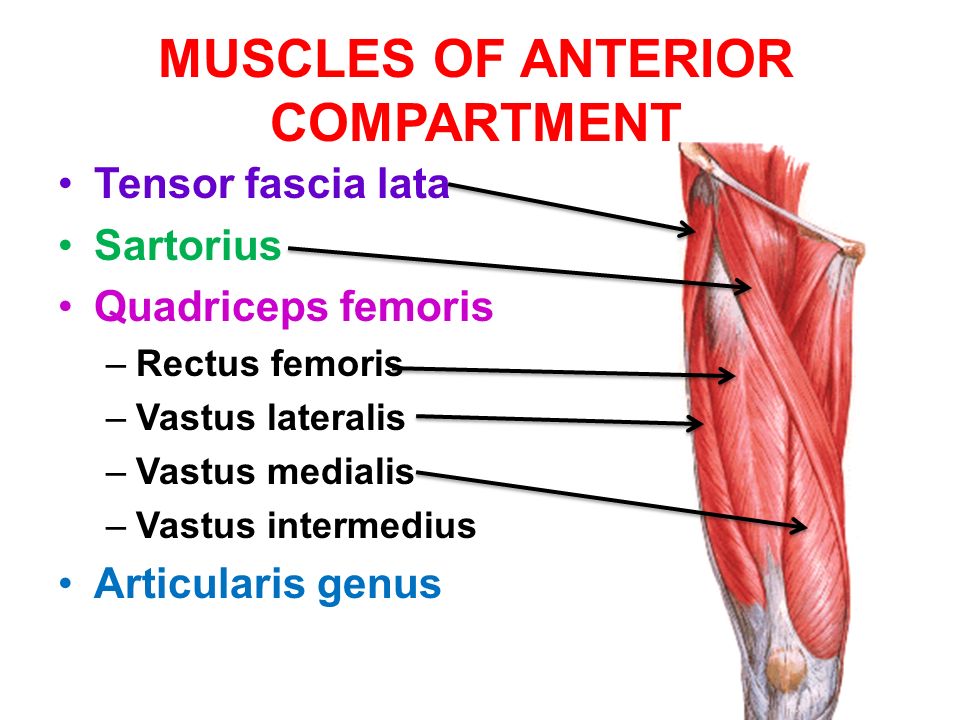
Muscles of the anterior compartment of the thigh
- Sartorius
- Quadriceps femoris
Sartorius: The sartorius is the longest muscle in the human body. It is a long, thin, superficial muscle that extends down the length of the thigh in the anterior compartment muscles.
Origin: Anterior superior iliac spine
Insertion: Upper medial surface of the shaft of the tibia in front of the insertions of the gracilis and the semitendinosus
Nerve supply: Femoral nerve
Action:
Abductor of thigh
Lateral rotator of thigh
Flexor of the leg at knee joint
Quadriceps Femoris: The quadriceps femoris also called the quadriceps, quadriceps extensor, or quads is the large muscle group that includes the four muscles on the front of the thigh.
The quadriceps is the great extensor muscle of the knee, forming a large fleshy muscle group covering the front and sides of the thigh.
- Rectus Femoris
- Vastus Lateralis
- Vastus Medialis
- Vastus Intermedius
Rectus Femoris: The rectus femoris is one of the four quadriceps muscles. All four parts of the quadriceps muscle join the patella via the quadriceps tendon. The rectus femoris is situated in the middle of the front of the thigh.
- Origin:
Straight head: Anterior inferior iliac spine
Reflected head: Ilium above the acetabulum - Insertion: Quadriceps tendon ( RF, vastus lateralis, vastus medialis, vastus intermedius) into patella, then via ligamentum patellae into tubercle of the tibia.
- Nerve supply: Femoral nerve
- Action:
Flexor of hip joint
Extensor of knee joint
Vastus Lateralis: The vastus lateralis is the largest and most powerful part of the quadriceps, a muscle in the thigh. The vastus lateralis arises from a series of flat, broad tendons attached to the femur, and attaches to the outer border of the patella. The vastus lateralis is the suggested site for intramuscular injection in babies less than 7 months old.
- Origin:Upper part of intertrochanteric line
- Insertion: Quadriceps tendon into patella, then via ligamentum patellae into tubercle of tiba.
- Nerve supply: Femoral nerve
- Action: Extends knee joint
Vastus Medialis: The vastus medialis is an extensor muscle found medially in the thigh that extends the knee. The vastus medialis is part of the quadriceps.
- Origin: Lower part of the intertrochanteric line, the medial intermuscular septum and the aponeurosis of adductor Magnus.
- Insertion: Quadriceps tendon into patella, then via ligamentum patellae into tubercle of tibia.
- Nerve supply: Femoral nerve.
- Action: Extensor of the knee joint.
Vastus Intermedius: The vastus intermedius originated from the front and lateral surfaces of the body of the femur in its upper two-thirds, lying under the rectus femoris and from the lower part of the lateral intermuscular septum.
- Origin:Anterior and lateral surface of the shaft of the femur.
- Insertion: Quadriceps tendon into patella, then via ligamentum patellae into tubercle of tibia.
- Nerve supply: Femoral nerve
- Action: Extensor of knee joint
Weakness of the extensor muscles induces Hyperextended Knee.
Muscles of the Medial Compartment of Thigh
- Adductor Longus
- Adductor Brevis
- Adductor Magnus
- Gracilis
- Pectineus
Adductor Longus: The adductor longus muscle located in the thigh. One of the adductor muscles of the hip, innervated by the obturator nerve. The adductor longus forms the medial wall of the femoral triangle.
Origin: Body of the pubis in the angle between the pubic crest and the pubic symphysis
Insertion:Linea aspera
Nerve supply: Anterior division of obturator nerve
Action:
Powerful adductor of the thigh
Act as posture controllers
Adductor Brevis: The adductor brevis is located immediately deep to the pectineus and adductor longus. It belongs to the adductor group of the thigh muscles.
Origin:
The anterior surface of the body of the pubis
Outer surface of inferior ramus of the pubis
Outer surface of the ramus of ischium
Insertion: Linea aspera
Nerve supply: Anterior or posterior division of obturator nerve
Action:Adductor longus, adductor brevis and upper part of adductor magnus help in flexion of the thigh.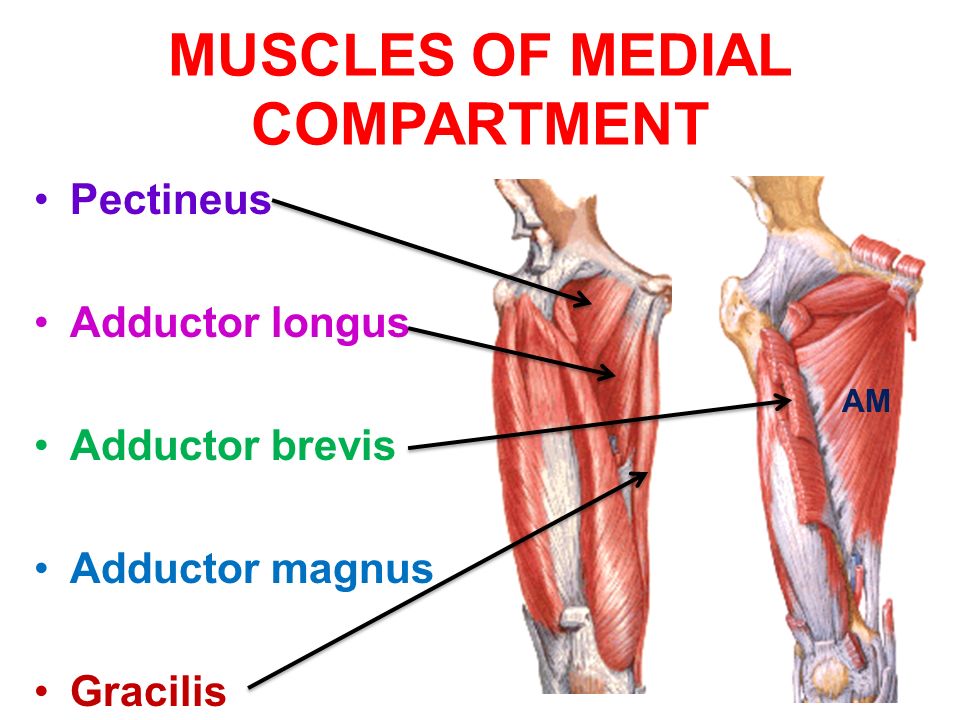
Adductor Magnus( hybrid muscle): The Adductor Magnus is a large triangular muscle, located on the medial side of the thigh. It consists of two parts.
Origin:
Ramus of the ischium
Lower part of inferior ramus of the pubis
Insertion: Linea aspera
Nerve supply: ( double nerve supply)
Adductor part: posterior division of obturator nerve
Hamstring part: tibial part of the sciatic nerve
Action:
Lower part of adductor magnus helps in
Extension of hip
Flexion of knee
Gracillis: The gracilis is the most superficial muscle on the medial side of the thigh.
Origin:
Inferior ramus of the pubis
Ramus of the ischium
Insertion: Upper part of medial surface of the shaft of the tibia
Nerve supply: Anterior division of obturator nerve
Action:
Flexor of thigh
Medial rotator of the thigh
Weak adductor of the thigh
Pectineus: The pectineus is a flat, quadrangular muscle situated at the anterior part of the upper and medial aspect of the thigh. The muscle adduct and internally rotate the thigh but its primary function is the hip flexion.
Origin: Superior ramus of the pubis
Insertion: Lesser trochanter to linea aspera
Nerve supply:( double nerve supply)
Anterior fibers: femoral nerve
Posterior fibers: anterior division of obturator nerve
Action:
Flexor thigh
Adductor of thigh
Muscles of the back of the thigh
- Semitendinosus
- Semimembranosus
- Biceps Femoris
- Adductor Magnus
Semitendinosus: The semitendinosus is a long superficial muscle in the back of the thigh muscles. It occupies posteromedially in the thigh, superficial to the semimembranosus.
Origin: Upper part of the ischial tuberosity
Insertion: Upper part of medial surface of the shaft of tibia behind the sartorius and the gracilis.
Nerve supply: Tibial part of the sciatic nerve
Action:
Chief flexor of knee
Weak extensor of hip
Semimembranosus: The semimembranosus is the most medial of the three hamstring muscles. The semimembranosus occupies posteromedially in the thigh, deep to the semitendinosus.
Origin: Upper part of the ischial tuberosity
Insertion: Medial condyle of tibia
Nerve supply: Tibial part of the sciatic nerve
Action:
Chief flexor of knee
Weak extensor of hip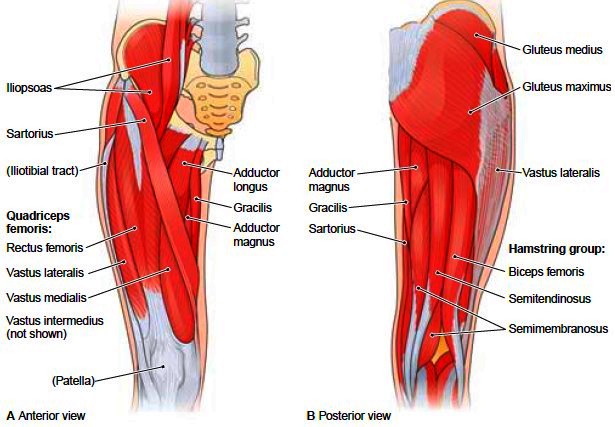
Biceps Femoris: The biceps femoris is a thigh muscle located in the posterior part of the thigh. It has two parts, one of which the long head of the biceps femoris forms part of the hamstrings muscle group.
Origin:
Long head:
Upper part of the ischial tuberosity
Short head:
Linea aspera
Upper 2/3rds of the lateral supracondylar line
Insertion: Head of the fibula
Nerve supply:
Long head: tibial part of the sciatic nerve
Short head: common peroneal part of the sciatic nerve
Action: Flexes the knee, and also rotates the tibia laterally; long head also extends the hip joint.
Movements of the Knee
There are four main movements that the knee joint permits:
Knee Extension: Produced by the quadriceps femoris (rectus femoris, vastus medialis, vastus lateralis and vastus intermedius); tensor fasciae latae.
Knee Flexion: Produced by the hamstrings (biceps femoris, semitendinosus and semimembranosus); popliteus; gracilis; sartorius.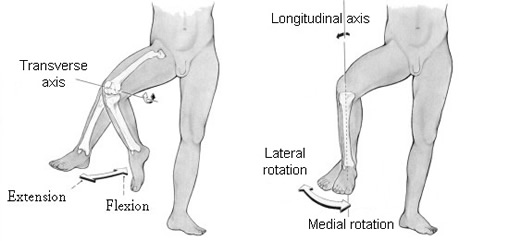
Knee Lateral rotation: Produced by the biceps femoris.
Knee Medial rotation: Produced by semimembranosus, popliteus, pes anserinus (semitendinosus, gracilis, sartorius).

