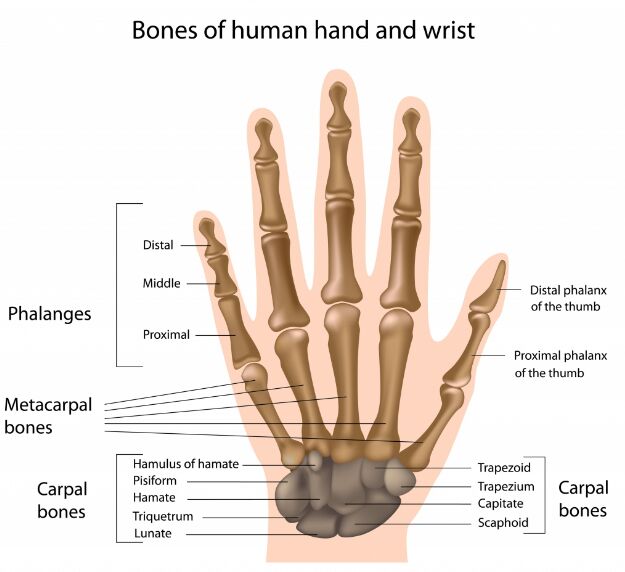
Hand Bones:The hand consists of 27 bones, the eight short carpal bones are arranged into a proximal row (scaphoid, lunate, triquetral and pisiform) which joins with the bones of the forearm, and a distal row (trapezium, trapezoid, capitate and hamate), which joins with the bases of the five metacarpal hand bones . They can be divided into three categories:
- Carpal bones – A eight irregularly shaped bones. The carpal hand bones are placed in the wrist area.
- Metacarpals – The five metacarpals, each one related to a digit.
- Phalanges – The Phalanges bones are located on the fingers. Each finger has three phalanges, except for the thumb, which becomes two.
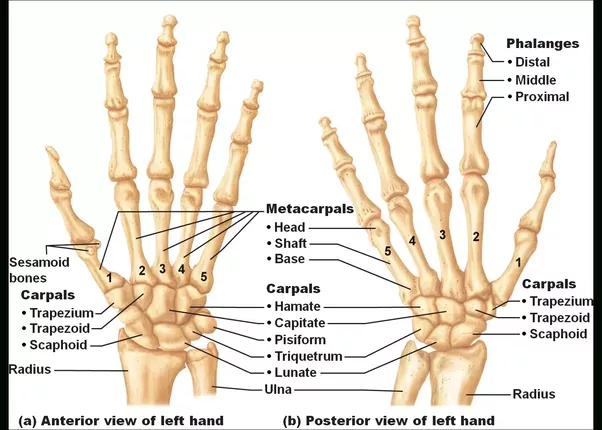
The heads of the metacarpals hand bones will each in turn articulate with the bases of the proximal phalanx of the fingers and thumb. These joints with the fingers are the metacarpophalangeal joints. The fourteen phalanges of hand bones make up the fingers and thumb and are numbered I-V (thumb to little finger) while the hand is observed from an anatomical position (palm up). The four fingers particular consist of three phalanges of the hand bones: proximal, middle, and distal phalanges. The thumb just consists of a proximal and distal phalanx.
Carpal Bones
Scaphoid
The scaphoid is a hand bone in the wrist. Maximum of the scaphoid is overlaid with cartilage which contacts five other bones in the wrist and forearm. The part of the scaphoid without cartilage is attached to ligaments and has blood vessels that come from the radial artery.
Lunate
The lunate is a bone in the middle of the wrist bones. It is almost entirely covered in cartilage. This bone has a crescent shape. It is uncommon to break, but the lunate can be involved with dislocations of the wrist.
Triquetrum
The triquetrum bone is the small finger side of the wrist bones. The triquetrum bone adds stability to the wrist.
Trapezoid
The trapezoid is a roughly trapezoidal-shaped bone in the second row of wrist bones and principally carries the index finger metacarpal bone in position. This bone is unusually injured.
Trapezium
The trapezium bone is a saddle-shaped in the second row of wrist bones. This bone stabilizes thumb. The two main problems are seen with this wrist bone. Fracture of the bone is common, although the most common problem is arthritis within the trapezium.
Capitate
The capitate is a large bone in the second row of the wrist bones. The capitate sits primarily under the middle finger metacarpal bone. The capitate bone makes a significant participation to wrist motion.
Hamate
The hamate is large, that has an almost triangular shape and is located in the second row of wrist bones. It holds up the ring and little finger metacarpal bones.
Pisiform
The pisiform is a small sesamoid bone that sits in the wrist and is in the flexor carpi ulnaris tendon. Infrequently, the pisiform can break or can have arthritis in the joint it initiates with the triquetrum.
Metacarpal Bones
The hand bones of the metacarpal join proximally with the carpals, and distally articulate with the proximal phalanges. They are numbered:
- Metacarpal I – Thumb
- Metacarpal II – Index finger
- Metacarpal III –Middle finger
- Metacarpal IV – Ring finger
- Metacarpal V – Little finger
Each hand bones of the metacarpal consist of a base, shaft and a head. The medial and lateral surfaces of the metacarpals bones are concave, providing attachment of the interossei muscles. There are two prevalent fractures linked with metacarpal bones – Boxer’s fracture and Bennett’s fracture.
Phalanges
The phalanges are the hand bones of the fingers. There are three phalanges in four of the fingers while the thumb has a proximal and distal phalanx.

