Leg Muscles: The lower leg muscles comprise the three compartment-Anterior Compartment, Lateral Compartment, and the Posterior Compartment.
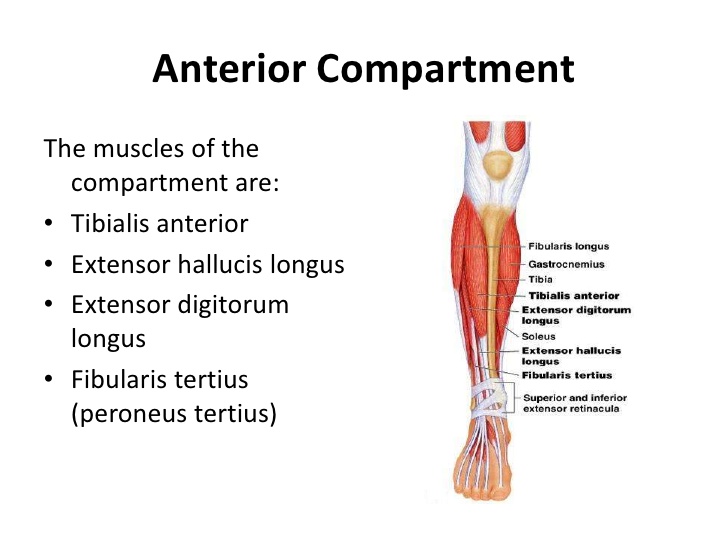
Anterior Compartment Leg Muscles
The anterior compartment of the leg comprises four muscles. The anterior compartment of the leg acts to dorsiflex and invert the foot through the ankle joint. The extensor hallucis longus and the extensor digitorum longus also extend the toes. The anterior compartment of the leg muscles is innervated by the deep fibular nerve (L4-L5) and supplied blood via the anterior tibial artery.
- Tibialis anterior
- Extensor hallucis longus
- Extensor digitorum longus
- Peroneus tertius
Tibialis anterior: The tibialis anterior muscle is mostly located near the shin. Tibialis anterior originates in the upper two-thirds of the lateral surface of the tibia and inserts into the medial cuneiform and first metatarsal bones of the foot. The tibialis anterior works to dorsiflex and invert the foot.
Origin:
Lateral condyle of tibia
Upper 2/3rd or less of the lateral surface of the shaft of the tibia
Interosseous membrane
Insertion:
Medial cuneiform
Base of the first metatarsal bone
Nerve supply: Deep peroneal nerve
Action:
Dorsiflexor of foot
Invertor of foot
Extensor hallucis longus: The Extensor hallucis longus is a thin muscle, situated within the Tibialis anterior and the Extensor digitorum longus muscles. The Extensor hallucis longus is located on the lateral side of the leg.
Origin:
Medial surface of the shaft of fibula
Interosseous membrane
Insertion: Dorsal surface of the base of the distal phalanx of the great toe
Nerve supply: Deep peroneal nerve
Action:
Dorsiflexor of foot
Extends metatarsophalangeal and interphalangeal joints of the great toe
Extensor digitorum longus: The extensor digitorum longus muscle is situated at the lateral part of the front of the leg. The muscle performs several movements of the ankle and the toes.
Origin:
Lateral condyle of tibia
Medial surface of the shaft of fibula
Interosseous membrane
Insertion:
Bases of the middle and distal phalanges
Nerve supply: Deep peroneal nerve
Action:
Dorsiflexor of foot
Extends metacarpophalangeal, proximal and distal interphalangeal joints of 2nd -5th toes
Peroneus Tertius: The peroneus tertius muscle is located in the lower limb. The Peroneus Tertius also was known as fibularis tertius.
Origin:
Lower 1/4th of the medial surface of the shaft of the fibula
Interosseous membrane
Insertion: Medial part of the dorsal surface of the base of the 5th metatarsal bone
Nerve supply: Deep peroneal nerve
Action:
Dorsiflexor of foot
Evertor of foot
Lateral Compartment Leg Muscles
The lateral compartment of the leg muscles is; peroneal longus and brevis.The common function of the peroneal muscles is eversion. Both muscles are innervated by the superficial fibular nerve.
- Peroneus longus
- Peroneus brevis
Peroneus longus: The peroneus longus ( fibularis longus) is a superficial muscle in the lateral compartment of the leg and works to evert and plantarflex of the ankle joint.
Origin:
Head of the fibula
Lateral condyle of the tibia
Lateral surface of the shaft of the fibula
Insertion:
Lateral side of the base of the 1st metatarsal bone
Medial cuneiform bone
Nerve supply: Superficial peroneal nerve
Action:
Evertor of foot
Maintain lateral longitudinal arch and transverse arch of the foot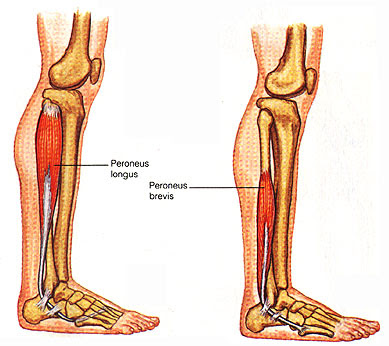
Peroneus brevis: The peroneus brevis lies below the cover of the peroneus longus, and is the shorter and smaller of the peroneus muscles.
Origin: Lateral surface of the shaft of fibula
Insertion: Lateral side of the base of the 5th metatarsal bone
Nerve supply: Superficial peroneal nerve
Action: Evertor of foot
Posterior Compartment Leg Muscles
The posterior compartment of the leg comprises seven muscles, organized into two layers – superficial and the deep. The two layers are divided by a band of the fascia.
Superficial Muscles:
- Gastrocnemius
- Plantaris
- Soleus
Gastrocnemius: The gastrocnemius muscle is the two-headed that is in the back part of the lower leg. It goes from just above the knee to the heel, a two joint muscle. Gastrocnemius forms the major mass at the posterior of the lower leg and is an extremely powerful muscle.
Origin: it has two head
medial head: medial condyle of the femur
lateral head: lateral condyle of the femur
Insertion: Middle 1/3rd of the posterior surface of the calcaneum
Nerve supply: Tibial nerve
Action: Planter flexors of the foot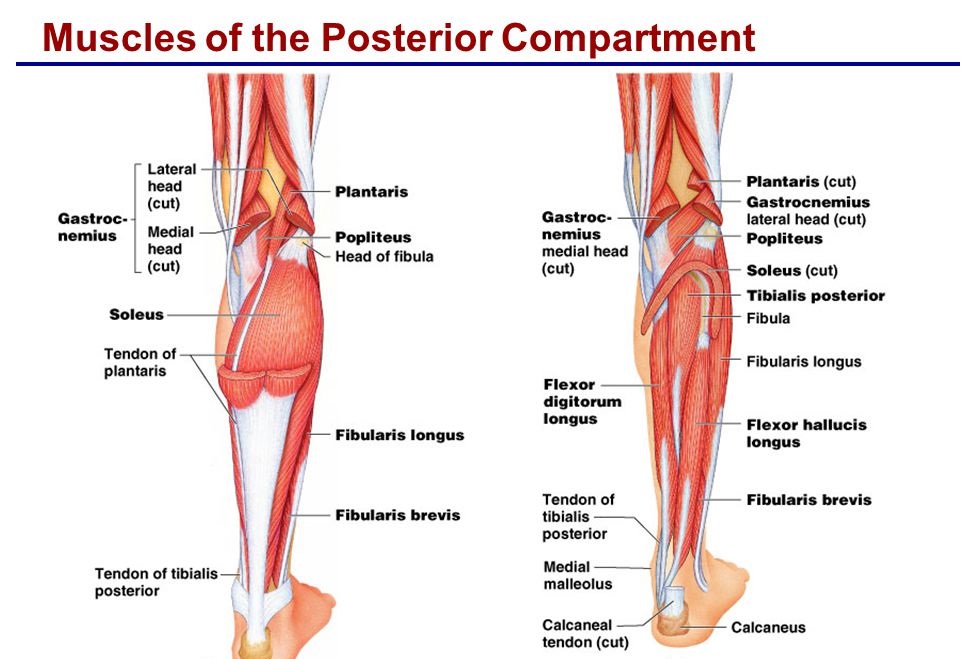
Soleus: The soleus Located in the superficial posterior compartment of the leg and it is a powerful muscle in the back part of the leg. It covers from just below the knee to the heel, and is committed to standing and walking.
Origin:
shaft of the tibia
shaft of the fibula
Insertion: Middle 1/3rd of the posterior surface of the calcaneum
Nerve supply: Tibial nerve
Action:
Planter flexors of foot
Important in walking and running
Plantaris: The plantaris is a superficial muscle of the posterior compartment of the leg.
Origin: Lateral supracondylar line of the femur
Insertion: Posterior surface of the calcaneum
Nerve supply: Tibial nerve
Action:
Plantaris is a rudimentary muscle.
Functional importance is of transplantation.
Deep Muscles:
Popliteus: The Popliteus is a small muscle positioned at the back of the knee joint. The popliteus muscle in the leg is utilized for unlocking the knees during walking. It is too worked when sitting down and standing up. It is the unique muscle in the posterior compartment of the leg that works just on the knee and not on the ankle joint.
Origin: Lateral condyle of the femur
Insertion: Posterior surface of the shaft of tibia
Nerve supply: Tibial nerve
Action:Unlocks knee joint by lateral rotation of femur
Tibialis Posterior: The tibialis posterior muscle is placed in the deep posterior compartment of the lower leg. It is the chief stabilizing muscle of the leg. The tibialis posterior innervated by tibial nerve and blood is supplied to the muscle by the posterior tibial artery.
Origin:
Posterior surface of shaft of tibia
Posterior surface of shaft of fibula
Insertion: Tuberosity of navicular bone
Nerve supply: Tibial nerve
Action:
Plantar flexor of ankle joint
Inverts foot at subtalar joint.
Flexor Digitorum Longus: The flexor digitorum longus is located on the tibial side of the leg.
Origin:Posterior surface shaft of tibia
Insertion:Bases of distal phalanges of shaft of lateral four toes
Nerve supply:Tibial nerve
Action:
Flexes distal phalanges
Plantar flexor of ankle joint
Flexor Hallucis Longus: The flexor hallucis longus muscle is deep muscles of the posterior compartment of the leg that connects to the plantar surface of the distal phalanx of the great toe.
Origin: Posterior surface of the shaft of the fibula
Insertion: Plantar surface of the base of distal phalanx of the great toe
Nerve supply: Tibial nerve
Action:
Flexes distal phalanx of the great toe
Plantar flexor of ankle joint

