Facial Muscles: The facial muscles are a group of skeletal muscles lying under the facial skin & supplied by the facial nerve (cranial nerve VII) that control facial expression. The facial muscles are also described as mimetic muscles. The facial muscles can broadly be split into three groups; orbital, nasal and oral.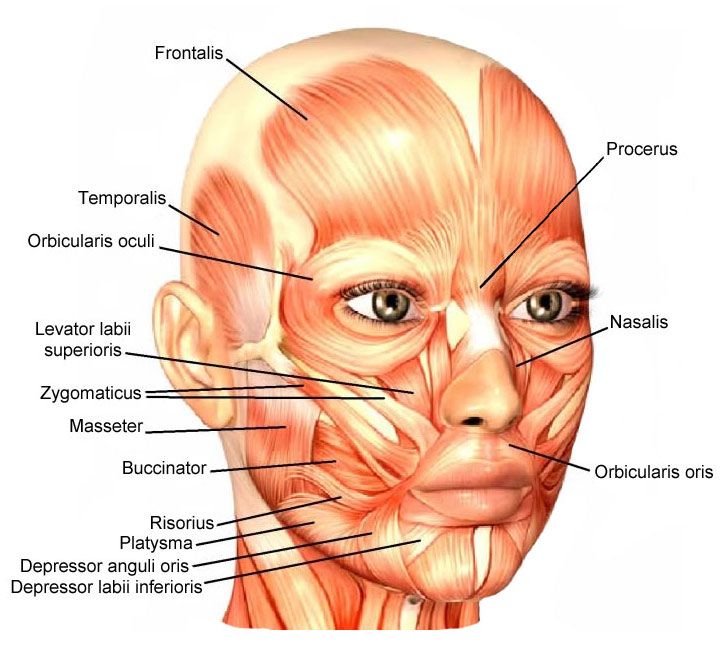
Orbital Group
The orbital group of the facial muscles comprises two muscles that control the movements of the eyelids and protect the cornea from damage. They are both innervated by the facial nerve.
Orbicularis oculi: The orbicularis oculi is a muscle in the face that closes the eyelids. The orbicularis oculi can be functionally split into two parts; inner palpebral part and the outer orbital part.
Origin: Frontal bone and Maxilla
Insertion: Eyelid
Action: The palpebral part gentle closure of the eyelid, whereas the orbital portion closes more forcefully.
Corrugator Supercilii: The corrugator supercilii is located posteriorly to the orbicularis oculi muscle.
Origin: It originates from the superciliary arch, running in a superolateral direction.
Insertion: It inserts into the skin of the eyebrow.
Actions: Draw the eyebrows together, creating vertical wrinkles on the bridge of the nose.
Nerve Supply: Facial nerve.
Nasal Group
The nasal group of facial muscles is associated with movements of the nose. There are three muscles-Nasalis, Procerus &Depressor Septi Nasi in this group, and all muscles are innervated by the facial nerve.
Nasalis: The nasalis is the biggest of the nasal muscles. The nasalis divided into two parts; transverse and alar.
Origin: Both parts of the nasalis muscle arise from the maxilla.
Insertion: The transverse part joins to an aponeurosis across the dorsum of the nose. The alar portion of the muscle connects to the alar cartilage of the nasal skeleton.
Actions: The two parts of the nasalis have opposing functions. The transverse part compresses the nares, and the alar part opens the nares.
Nerve Supply: Facial nerve.
Procerus: The procerus is the most superior of the nasal muscles.
Origin: It originates from the nasal bone.
Insertion: It inserting into the lower medial forehead.
Actions: Contraction of Procerus muscle pulls the eyebrows downward to allow transverse wrinkles over the nose.
Nerve Supply: Facial nerve.
Depressor Septi Nasi: This muscle supports the alar part of the nasali in opening the nostrils.
Origin: The Depressor Septi Nasi runs from the maxilla (above the medial incisor tooth).
Insertion: It inserts to the nasal septum.
Function: It pulls the nose inferiorly, opening the nares.
Nerve Supply: Facial nerve.
Oral Group
These are the most important group of the facial expressions – they are responsible for movements of the mouth and lips. Such movements are needed in singing and whistling and add emphasis to vocal communication. The oral group muscles consist of the orbicularis oris, buccinator, and various smaller muscles.
Orbicularis Oris:
Origin: Maxilla and mandible
Insertion: Skin and muscle around the mouth
action: Closes lips (purses, protrudes)
Buccinator:
Origin: Mandible and maxilla (molar regions)
insertion: Orbicularis Oris
Action: Compress cheeks (whistling, sucking)
Frontalis:
Origin: Epicranial aponeurosis
Insertion: Skin of eyebrows
Action: Raise eyebrows
Zygomaticus major:
origin: Zygomatic bone
Insertion: Skin and muscle at the corner of the mouth.
Action: Raises corners of the mouth (smile)
Muscles that act on the Jaw (for mastication and facial expression)
Masseter:
origin: Zygomatic arch and Bone
Insertion: Mandible ramus and Angle
Action: Elevates mandible (as in the closing mouth while chewing)
Temporalis:
Origin:Temporal, frontal & parietal bones
insertion: Coronoid process of Mandible
Action: Elevates mandible
Platysma:
origin: Pectoralis muscle
Insertion: Mandible, the skin of the lower face
Action: Pulls lower lip down (as in frowning), Depresses mandible (opening mouth as when chewing or surprised)
Others Facial Muscles-
- Occipitofrontalis muscle
- Depressor supercilii muscle
- Auricular muscles (anterior, superior and posterior)
- Depressor anguli oris muscle
- Risorius
- Zygomaticus major muscle
- Zygomaticus minor muscle
- Levator labii superioris
- Levator labii superioris alaeque nasi muscle
- Depressor labii inferioris muscle
- Levator anguli oris
- Mentalis

